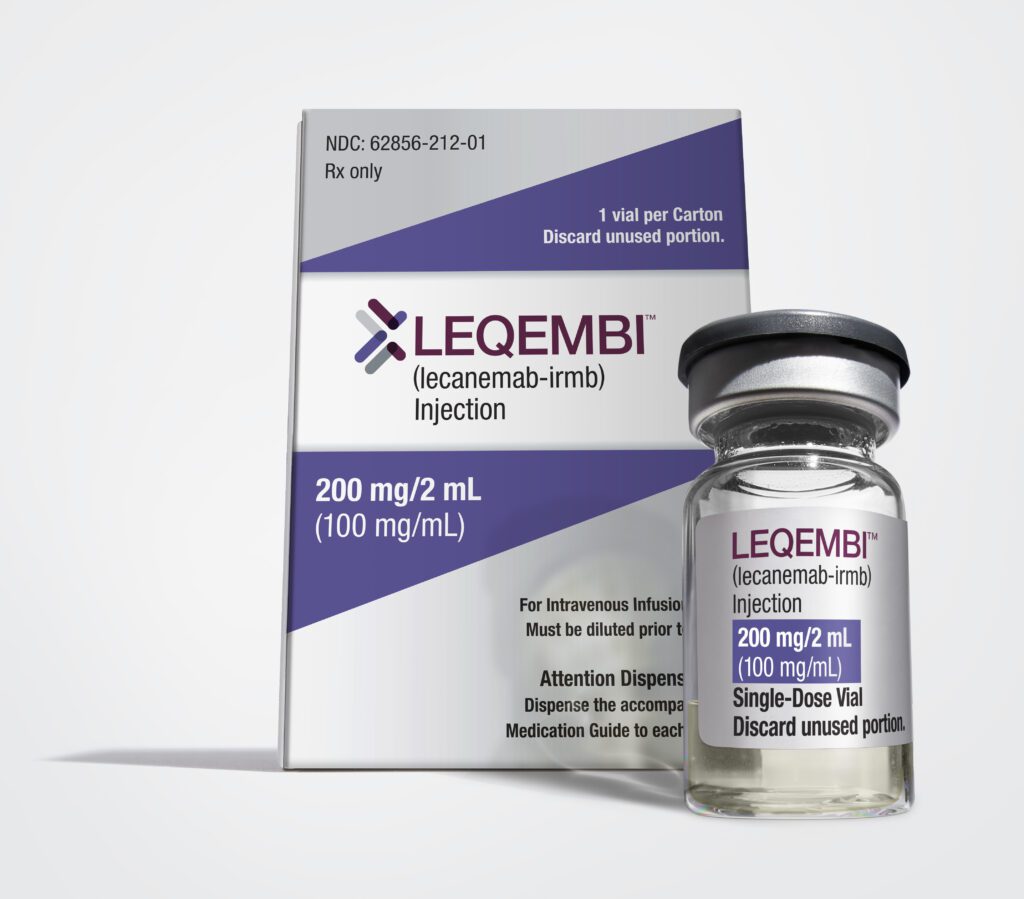
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on Friday granted accelerated approval for the Alzheimer’s drug LEQEMBI (lecanemab-irmb).
The drug is developed by two biotech companies, Eisai and Biogen, both members of the Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO).
This is the second treatment from Eisai in partnership with Biogen to receive an early green light in less than two years, according to CNBC.
This decision means the drug is the second of a new category of medications approved for Alzheimer’s that target the fundamental pathophysiology of the disease, following Biogen’s Aduhelm in 2022.
What you should know about LEQEMBI
The approval is based on phase 2 clinical trial data that showed LEQEMBI decreased the buildup of A plaque in the brain, a characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
According to the FDA, the drug is suitable for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia stage of Alzheimer’s disease.
“This treatment option is the latest therapy to target and affect the underlying disease process of Alzheimer’s, instead of only treating the symptoms of the disease,” shared Dr. Billy Dunn, director of the Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
Following the announcement, Eisai submitted a Supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) to the FDA for approval via the conventional channel. This application used newly released data from the significant global confirmatory phase 3 clinical trial, Clarity AD.
Alzheimer’s study shows progress
The FDA recently announced the findings of a phase 3 randomized controlled clinical trial to verify the drug’s clinical benefit and said it expects to receive the data shortly.
Researchers assessed LEQEMBI’s effectiveness in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study with 856 Alzheimer’s patients. The researchers have started treatment in patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia.
Patients who received the recommended dose of lecanemab, 10 mg/kilogram every two weeks, saw a considerable reduction in the amount of amyloid beta plaque, which was time- and dose-dependent. Compared to the placebo arm, which had no reduction in amyloid-beta plaque, it demonstrated a statistically significant decrease in brain amyloid plaque from baseline to Week 79.
“The FDA’s approval of LEQEMBI under the Accelerated Approval pathway is an important milestone in Eisai’s four decades of research in Alzheimer’s disease and reflects our continued commitment to alleviating the burden of Alzheimer’s disease for patients and their families. Eisai has made great efforts to understand the reality of the challenges and concerns facing patients and their families who are living in the various stages of Alzheimer’s disease, and we are incredibly pleased to offer LEQEMBI as a new treatment option to help with the tremendous unmet needs of this community,” said Haruo Naito, Chief Executive Officer at Eisai Co., Ltd.
“The approval of LEQEMBI provides new hope to patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Patients at an early stage of the disease and their caregivers can now consider a new treatment option with their doctors. Our focus now is on the path forward, working alongside Eisai with the goal of making LEQEMBI available to patients who may benefit from this treatment as soon as possible,” said Christopher A. Viehbacher, President and Chief Executive Officer of Biogen.
The recommended dosage of LEQEMBI is 10 mg/kg, administered intravenously once every two weeks to eligible patients with confirmed presence of Aβ pathology before initiating treatment. Enhanced clinical vigilance for amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) is recommended during the first 14 weeks of therapy with LEQEMBI, said the press release from Eisai.