Regulatory improvements and support for biotechnology research were among the actions that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced Wednesday as part of the National Biotechnology and Biomanufacturing Initiative (NBBI).
The initiative, launched Monday through President Biden’s executive order, will spend an estimated $2 billion on a “whole-of-government approach to advance biotechnology and biomanufacturing.”
HHS outlined a range of actions that it will be taking under the initiative, to “help drive research and development, expand market opportunities for biobased products, streamline regulatory processes for products of biotechnology, and build a thriving and secure global bioeconomy with partners and allies.”
Specific HHS actions under the initiative
On the global level, the HHS would “lead international regulators in harmonizing requirements to promote innovation.”
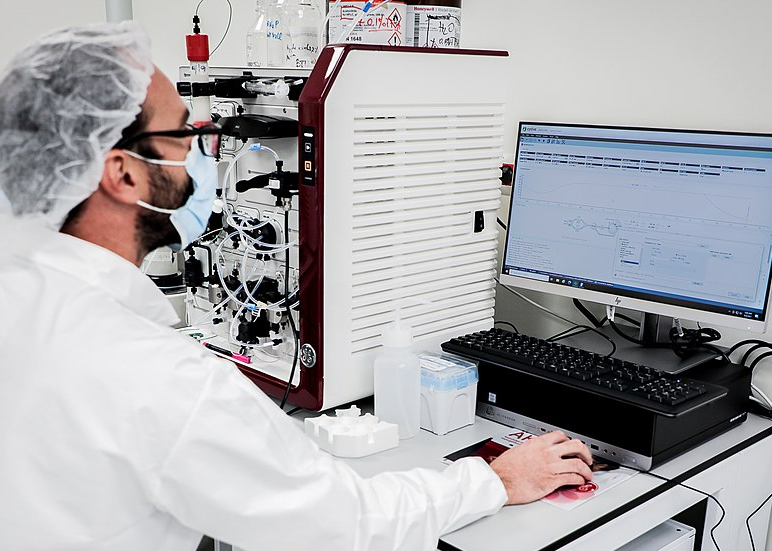
Several changes that could impact the drug approval process involve enhancements or new approaches within two Food and Drug Administration (FDA) offices, the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) and the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER):
- Supporting research of advanced manufacturing technologies in the centers, “to build a knowledge base in support of regulatory assessment, as well as scientific standard, guidance, and policy development.”
- Supporting development of the FDA Center for Advancement of Manufacturing Pharmaceuticals to enhance collaboration between CDER and CBER.
- Pre-submission support from CDER, CBER and other FDA offices, “for applicants looking to adopt advanced manufacturing technologies.”
HHS also announced support for researchers, including:
- Supporting the “development of innovative animal products produced with biotechnology” for both agricultural and biopharmaceutical use, via the Veterinary Innovation Program (VIP) at the FDA’s Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM).
- Continuing support of pilots-programs such as the NCATS-led Platform Vector Gene Therapy (PaVe-GT), which “seeks to increase the efficiency of clinical trial startup by using the same gene delivery system and manufacturing methods for multiple rare disease gene therapies.”
- Expanding cell engineering capabilities and establishing synthetic biology approaches and supporting and expanding cell engineering capabilities and platforms “through programs such as the Biopharmaceutical Development Program at the Frederick National Lab which is developing a new cell line to treat acute myeloid leukemia.”
The initiative also contains national security and pandemic preparedness components, including:
- Supporting development of the Advanced Manufacturing Innovation Hub in the FDA’s Office of Counterterrorism and Emerging Threats.
- “Collaborating with the Department of Defense to invest $1 billion in bio- industrial domestic manufacturing infrastructure” to produce products that are important to defense.
- Investing $40 million in biomanufacturing active pharmaceutical ingredients and antibiotics for the next pandemic.
- A Biosafety and Biosecurity Innovation Initiative, involving the National Institutes of Health, “to reduce the risk associated with advances in biotechnology, biomanufacturing, and the bioeconomy.”